What Language in The Netherlands: A Comprehensive Guide to Linguistic Diversity
What language in The Netherlands do you need to learn as an expat? If you're moving to The Netherlands, you're probably curious about the main languages spoken here. This article will explore the diverse languages you'll encounter, help you understand regional dialects, and offer tips on integrating into Dutch society. By the end of this guide, you'll be better prepared to communicate, connect, and thrive in your new home.
Introduction to the Languages of The Netherlands
The Netherlands is renowned for its linguistic diversity. While Dutch is the primary language, the country is home to a mosaic of regional dialects and minority languages. Understanding this linguistic landscape is crucial for expats who wish to integrate smoothly and make the most of their Dutch experience.
Dutch is a West Germanic language that evolved from Old Frankish and has been influenced by Latin, French, and German over the centuries. The earliest known written records in Old Dutch date back to around the 6th century. The language has since undergone significant transformations through Middle Dutch (12th-15th centuries) to the Modern Dutch spoken today.
The Dutch Language: An Overview
What language in The Netherlands is most widely spoken?
The answer is Dutch, or "Nederlands," which serves as the official language of The Netherlands. Let's delve deeper into its history, characteristics, and current use:
Characteristics of the Dutch Language
- Phonetics: Dutch phonetics can be challenging for non-native speakers, particularly the guttural sounds, such as the 'g' and 'ch'.
- Grammar: Dutch grammar includes gendered nouns (masculine, feminine, and neuter), with two grammatical cases (common and neuter) still in use. The language employs a Subject-Verb-Object (SVO) word order.
- Vocabulary: Dutch has a rich vocabulary influenced by other languages, especially French and English. This makes learning Dutch somewhat easier for English speakers due to shared roots and similar words.
Modern Use and Prevalence
Dutch is spoken by over 17 million people in The Netherlands and serves as the primary language for education, government, and media. It is also one of the official languages of the European Union and the Union of South American Nations, reflecting its global significance.
Dialects and Variations
Dutch has numerous dialects that vary regionally. Some prominent ones include Hollandic (spoken in North and South Holland), Brabantian (spoken in North Brabant and parts of Belgium), and Limburgish (spoken in Limburg). These dialects can differ significantly from standard Dutch, which is based on the Hollandic dialect and is known as "Algemeen Nederlands" (General Dutch).
The Influence of Dutch Abroad
Beyond The Netherlands, Dutch is spoken in Belgium (where it is known as Flemish), Suriname, Aruba, Curaçao, and Sint Maarten. In these regions, Dutch often coexists with other local languages, contributing to a rich linguistic blend.
Dutch in Education and Business
Dutch is the medium of instruction in schools and universities in The Netherlands. It is also the primary language of business and professional settings. For expats, proficiency in Dutch can open doors to job opportunities and deeper social integration.
Dutch, or "Nederlands," is the official language of The Netherlands. Spoken by over 90% of the population, Dutch is a West Germanic language with a rich history. It is the primary medium for education, government, and daily communication. Expats will find that mastering Dutch is essential for navigating life in The Netherlands.
The Second Official Language: Frisian
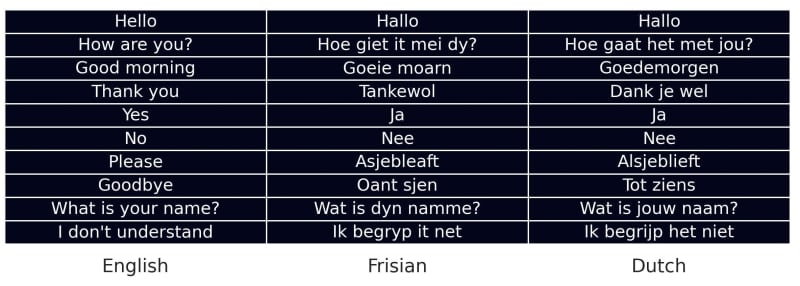
In addition to Dutch, Frisian (or "Frysk") holds official status in the province of Friesland. With a history dating back to the early Middle Ages, Frisian is closely related to English and has approximately 500,000 speakers. Understanding Frisian can offer deeper insights into the cultural heritage of Friesland and enhance your experience in this unique region.
Regional Dialects and Minority Languages
The Netherlands is a country rich in linguistic diversity beyond its primary language, Dutch. This diversity is embodied in its numerous regional dialects and minority languages. Understanding these languages can significantly enhance an expat's experience, providing deeper insights into the local culture and traditions.
Limburgish (Limburgs)
Where It's Spoken: Limburgish is primarily spoken in the southeastern province of Limburg. This dialect group includes several varieties that differ slightly from one region to another within the province.
Linguistic Characteristics: Limburgish is a dialect of the Low Franconian languages, closely related to Dutch and German. It has unique phonetic features, including the use of tones, which are rare in European languages. Limburgish uses a tonal distinction to differentiate meaning, similar to Mandarin Chinese.
Cultural Significance: The use of Limburgish is a strong marker of regional identity. It is often used in informal settings, local media, and cultural expressions such as music and literature. Understanding and speaking Limburgish can endear an expat to the local population, showing respect for their regional culture.
Low Saxon (Nedersaksisch)
Where It's Spoken: Low Saxon is spoken in the northeastern provinces of Groningen, Drenthe, Overijssel, and parts of Gelderland. It also extends into northern Germany.
Linguistic Characteristics: Low Saxon is part of the Low German dialect group and is quite distinct from standard Dutch. It has preserved many archaic features that have disappeared from Dutch and German, making it linguistically significant.
Cultural Significance: Like Limburgish, Low Saxon is an essential part of the regional identity in the northeastern Netherlands. It is used in local media, folklore, and festivals. Efforts to preserve and promote Low Saxon have led to its recognition as a regional language under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages.
Frisian (Frysk)
Where It's Spoken: Frisian is predominantly spoken in the province of Friesland (Fryslân). It has official status alongside Dutch in this province.
Linguistic Characteristics: Frisian is closely related to English and Scots, belonging to the West Germanic language family. It is known for its rich vowel system and distinctive sound patterns that set it apart from Dutch.
Cultural Significance: Frisian is a critical component of Friesland's cultural heritage. It is used in education, local government, and media. Knowledge of Frisian can provide expats with a deeper appreciation of Friesland’s unique cultural landscape.
Brabantian (Brabants)
Where It's Spoken: Brabantian is spoken in the provinces of North Brabant and the northern part of Belgian Brabant.
Linguistic Characteristics: Brabantian is a dialect of Dutch, with distinctive phonological and lexical features. It often uses softer pronunciations compared to standard Dutch and includes many French loanwords due to historical influences.
Cultural Significance: Brabantian is widely spoken in informal settings and local cultural activities. It plays a vital role in regional identity, and understanding it can help expats integrate more effectively into the social fabric of North Brabant.
Zeelandic (Zeeuws)
Where It's Spoken: Zeelandic is spoken in the province of Zeeland.
Linguistic Characteristics: Zeelandic dialects are part of the Dutch dialect continuum but show significant influences from West Flemish. They feature unique vowel sounds and grammatical structures.
Cultural Significance: Zeelandic is a strong cultural marker in Zeeland, used in local literature and festivals. Knowing some Zeelandic phrases can help expats connect with the locals on a more personal level.
Other Minority Languages
Yiddish:
Historically, Yiddish was spoken by the Ashkenazi Jewish community in The Netherlands, particularly in Amsterdam. While its use has declined, it remains a vital part of the Jewish cultural heritage in the country.
Papiamento:
In the Caribbean Netherlands, particularly in Bonaire, Papiamento is widely spoken. It is a creole language with elements from Portuguese, Spanish, Dutch, and African languages. Understanding Papiamento is essential for expats in these regions to engage with the local community.
The Role of English in The Netherlands
English is widely used in The Netherlands, especially in business, education, and tourism. The country ranks highly in English proficiency, making it easy for expats to communicate. However, learning Dutch is important for deeper integration and understanding local customs.
Importance in Business:
English is widely used in the business sector in The Netherlands. Many multinational companies have their European headquarters in Dutch cities such as Amsterdam and Rotterdam, and English is often the preferred language for corporate communication. This is particularly true in industries like finance, technology, and international trade. Business meetings, reports, and emails are frequently conducted in English, making it easier for expats to work and collaborate with Dutch colleagues and international partners.
Prevalence in Education:
The Dutch education system places a strong emphasis on learning English from a young age. English is a mandatory subject in primary and secondary schools, ensuring that most Dutch people have a good command of the language by the time they reach adulthood. Additionally, many universities offer a wide range of degree programs taught entirely in English, attracting a significant number of international students. This focus on English in education not only facilitates academic exchange but also prepares students for global careers.
Tourism and Everyday Life:
In the tourism industry, English is the primary language used to communicate with international visitors. Tourist information centers, museums, hotels, restaurants, and public transportation systems typically provide services and information in English. This widespread use of English makes it easy for tourists and newly arrived expats to navigate the country, access services, and enjoy their stay.
Language Learning Tips for Expats
Learning Dutch can greatly enhance your experience as an expat in The Netherlands, helping you integrate more deeply into the local culture and community. Here are some practical tips to get you started on your language-learning journey:
- Enroll in Language Courses: Numerous institutions offer Dutch language courses tailored for expats.
- Practice Regularly: Engage in conversations with locals to improve your fluency.
- Utilize Language Apps: Apps like Duolingo and Babbel can supplement your learning.
- Immerse Yourself: Watch Dutch TV shows, listen to Dutch music, and read Dutch newspapers.
- Join Expat Groups: Connect with other expats to share tips and practice the language together.
FAQs About Languages in The Netherlands
- What language is primarily spoken in The Netherlands?
Dutch is the primary and official language spoken by the majority of the population. - Is it necessary to learn Dutch as an expat?
While many Dutch people speak English, learning Dutch is essential for full integration and better opportunities. - What other languages are commonly spoken?
Frisian in Friesland, Limburgish in Limburg, and various regional dialects. - Is Frisian widely spoken outside Friesland?
Frisian is primarily spoken in Friesland and is not widely used outside this province. - How important is it to understand regional dialects in The Netherlands?
While not essential for daily life, understanding regional dialects can enhance your cultural experience and connection with locals. - How skilled are Dutch people in English?
The Netherlands ranks highly in English skill, with many Dutch people speaking it fluently. - Are there resources for learning Dutch?
Yes, there are numerous language courses, online apps, and community groups for learning Dutch. - What are some effective methods for learning Dutch?
Enrolling in language courses, practicing regularly, using language apps, immersing yourself in Dutch media, and joining expat groups.
Conclusion
Understanding what language in The Netherlands to learn and speak is vital for expats aiming to integrate and thrive. From Dutch and Frisian to regional dialects and the widespread use of English, the linguistic landscape of The Netherlands is diverse and fascinating. Embrace the opportunity to learn and connect through language, and your expat experience will be richer and more fulfilling.
Ready to dive deeper into Dutch culture and language?
Join Your Expat Social Club today and connect with fellow expats through our events and activities. Let us help you make the most of your new life in The Netherlands!










